TCP/IP, or the Transmission Control Protocol or Internet Protocol, is a collection of communicating protocols utilized for interconnecting network tools over the internet. TCP/IP may even be used as a broadcasting’s protocol in a personal PC network.
The whole IP set — a series of rules & processes — is usually denoted to as TCP/IP, although others are comprised in the set. The TCP/IP protocol set works as an extraction layer among internet applications & the routing/ substituting fabric.
TCP/IP, or the Transmission Control Protocol or Internet Protocol, is a collection of communicating protocols utilized for interconnecting network tools over the internet. TCP/IP may even be used as a broadcasting’s protocol in a personal PC network. identifies how data is switched on the internet by offering endways communication that recognize how it must be disturbed into packets, addressed, broadcasted, routed & accepted at the end. TCP/IP needs small central management, & it is intended to make networks dependable, with the capacity to automatically recover from the breakdown of any gadget on the network.
The 2 key protocols in the IP set provide particular functions. TCP describes how apps can establish channels for communication throughout a network. It even controls how a message is collected into smaller packets prior they are then communicated over the internet & reunited in the correct sequence at the end address.
IP explains how to address & send every packet to ensure it goes to the correct destination. Every gateway PC on the network verifies this IP address to ascertain where to send the message.
A subnet mask advises a PC, or any networking device, what section of the IP address is used in representing the network & what segment is used in representing hosts in the network.
How TCP/IP works?
TCP/IP utilities the user-server pattern of communication where a client or machine is specified a service (such as forwarding a web-page) by a new PC (a server) in the networks.
In a group, the TCP/IP set of protocols is categorized as homeless that means every client request is thought new as it is unconnected to last appeals. Being homeless frees up network tracks so they may be continuously used.
However itself the transport layer, is state full. It spreads a single message, & its connection stays in position until every packet in a message have been accepted & reunited at the end.
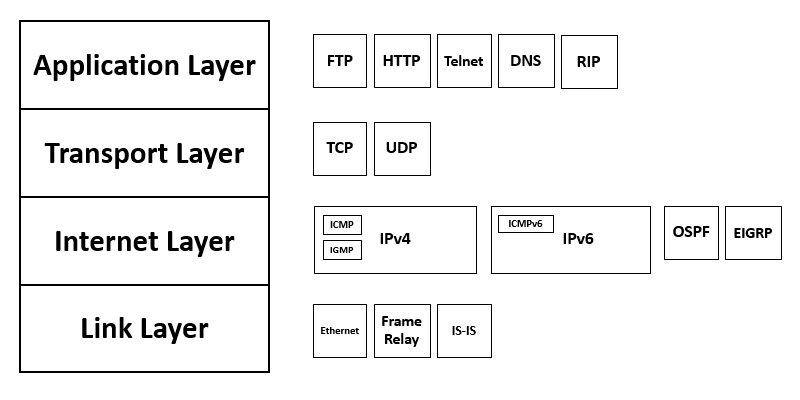
The TCP/IP model slightly differs from the 7-layers Open Systems Interconnections (OSI) network model planned after it. The reference OSI model outlines how apps can converse over the network.
TCP/IP may be used to offer reserved login on the network, for shared file transfer, to send email, to deliver web-pages on the networks & to distantly access file system of a server hosts.